A patent filed in the United State only protects your invention in US . The patent rights granted to you can be used to stop the making, using, selling or importation of infringing products in the US. However, if your US-patented invention is made abroad and only sold abroad, the US patent owner may not have any recourse against the infringer.
Additionally, you have to seek protection country by country. There is no such thing as a world wide patent. So, the decision to seek patent protection in other countries can be a tough one.
The major drawback that people encounter when exploring foreign patent protection is a limited budget. Seeking foreign patent protection can be very expensive. There are many different filing fees, translation costs, annuities, and legal fees for both your US and foreign patent attorneys.
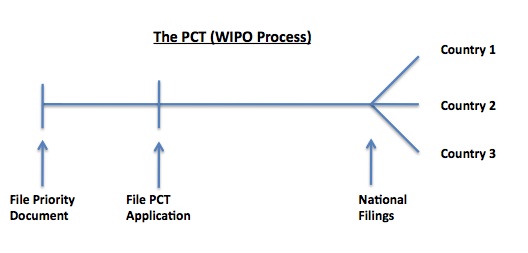
Above is the basic timeline for filing foreign patent protection. This is if you use the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) path. If you desire, you can just file in the individual countries, but that must be done within 12 months of filing any application, including a provisional application.



Patents
India is a member of the following International Organizations and Treaties in respect of patents:
- World Trade Organization (WTO) with effect from 01-01-1995.
- Convention establishing World Intellectual Property Organization, (WIPO).
- Paris Convention for the protection of Industrial Property with effect from Dec. 7, 1998.
- Patent Co-operation Treaty (PCT) with effect from Dec. 7, 1998.
- Budapest Treaty with effect from 17th December, 2001.
These treaties make it possible for Indian applicant (companies/ persons) to seek patent protection for an invention simultaneously in each of a large number of countries. Presently, two routes exist by means of which an Indian applicant may be able to file patents in foreign countries. These routes are:
- Paris Convention Route: Under this route, an applicant can file patents in any of the member countries within 12 months from making the first patent application in India. The following illustration explains the timeline for making foreign application:

PARIS CONVENTION TIMELINE
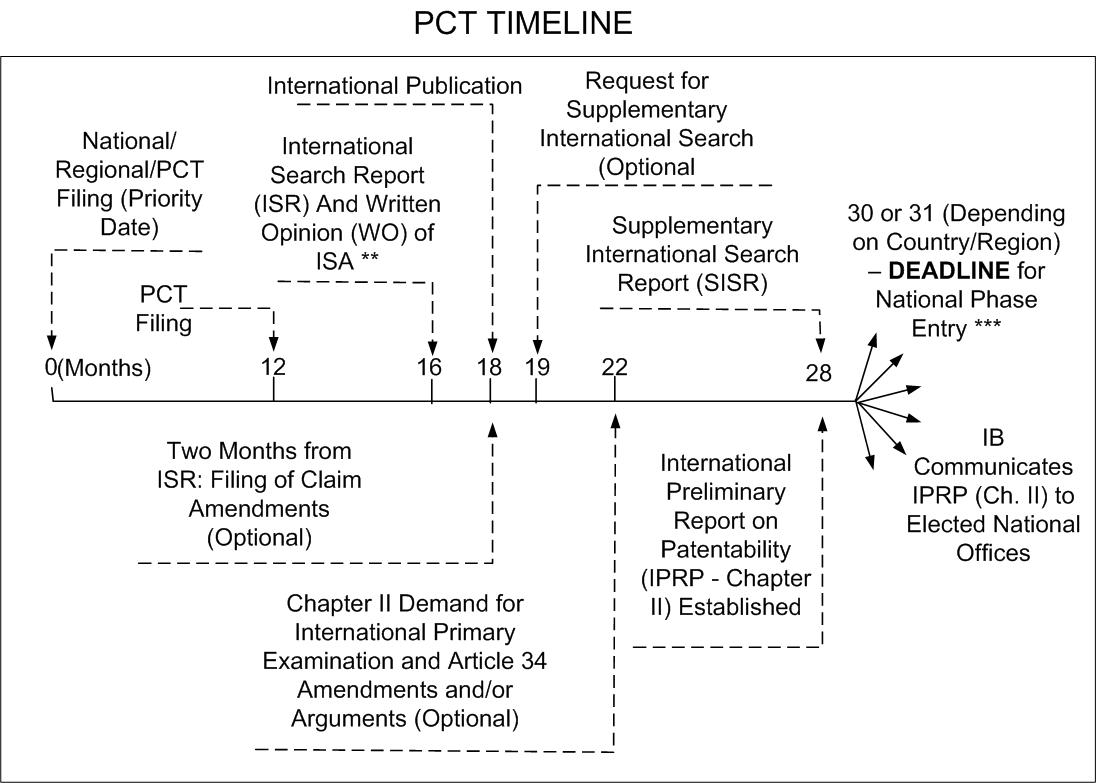
2. PCT Route: Under this route, an applicant is allowed to file a PCT application within 12 months from making the first patent application in India. The filing of the PCT application extends the time for filing in any of the PCT contracting members for the applicant to 30/31 months from the date of first filing. The following illustration explains the PCT timeline.
PCT TIMELINE
A PCT application may be filed by anyone who is a national or resident of India. It can be filed at the Indian patent office, or directly with the International Bureau of World Intellectual Property Organization, which administers the treaty, and is located in Geneva.
Importantly, the international application is subjected to what is called an “international search.” That search is carried out by one of the major patent offices, called the International Search Authorities (ISA). India is scheduled to soon become an ISA. The international search results in an “international search report,” that is, a listing of the citations of published documents that might affect the patentability of the invention claimed in the international application. In addition, a preliminary and non-binding, written opinion on whether the invention appears to meet the patentability criteria in light of the search report results is also issued.
The international search report and the written opinion are communicated to the applicant who, after evaluating their content, may decide to withdraw his application, in particular where the content of the report and opinion suggest that the granting of patents is unlikely, or he may decide to amend the claims in the application. This is the biggest advantage of using this route.
Designs
India is one of the countries party to the Paris Convention so the provisions for the right of priority are applicable. On the basis of Paris convention, a regular first application filed in one of the contracting state, the applicant may within the six months apply for protection in other contracting states; latter application will be regarded as if it had been filed on the same day as the first application. Please note that there is no registration authority that gives you a worldwide protection of your design.
Further, please note that since India is not a party to Hague Agreement, the benefits of filing single applications for designs (like a PCT) is not available to Indian nationals and companies.
Trademarks
Protection of trademarks internationally is done with the aid of the Madrid Protocol. A protection can be availed in all those countries to whose citizens India also provides protection by simply making a trademark application in those countries. Please note that there is no deadline to make corresponding trademark applications in such foreign countries.
The Protocol is managed by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO). Additionally, it also offers a trademark proprietor the possibility of having a mark protected in up to 77 countries and the European Community (EC) by filing one application, in one language (English, French or Spanish), with one set of fees, in one currency (Swiss Francs). The proprietors wishing to use the Madrid system must apply for trademark protection in a relevant national or regional trademark office before seeking international protection. Thereafter, the international registration can be maintained and renewed through a single procedure at WIPO.
Copyrights
The Berne Convention, which is administered by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) in Geneva, Switzerland and to which India is also a party, ensures that the copyrights of Indian nationals are well protected in all member countries that are party to the Berne Convention. However, please note that an author’s work is not automatically protected under “international copyright” throughout the world. Protection against unauthorized use usually depends on the national laws of a particular country. However, most countries do provide protection of foreign works under certain conditions and these conditions are specified by International copyright treaties and conventions.


Patent Cooperation Treaty ("PCT")
|
The PCT was concluded in 1970, amended in 1979, and modified in 1984 and 2001. It is open to States party to the Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property (1883). Instruments of ratification or accession must be deposited with the Director General of WIPO.
|
The Treaty makes it possible to seek patent protection for an invention simultaneously in each of a large number of countries by filing an "international" patent application. Such an application may be filed by anyone who is a national or resident of a Contracting State. It may generally be filed with the national patent office of the Contracting State of which the applicant is a national or resident or, at the applicant's option, with the International Bureau of WIPO in Geneva.
|
If the applicant is a national or resident of a Contracting State which is party to the European Patent Convention, the Harare Protocol on Patents and Industrial Designs (Harare Protocol), the revised Bangui Agreement Relating to the Creation of an African Intellectual Property Organization or the Eurasian Patent Convention, the international application may also be filed with the European Patent Office (EPO), the African Regional Industrial Property Organization (ARIPO), the African Intellectual Property Organization (OAPI) or the Eurasian Patent Office (EAPO), respectively.
|
The international application is then subjected to what is called an "international search." That search is carried out by one of the major patent offices appointed by the PCT Assembly as an International Searching Authority (ISA). The said search results in an "international search report," that is, a listing of the citations of such published documents that might affect the patentability of the invention claimed in the international application. At the same time, the ISA prepares a written opinion on patentability.
|
The international search report and the written opinion are communicated by the ISA to the applicant who may decide to withdraw his application, in particular where the said report or opinion makes the granting of patents unlikely.
If the international application is not withdrawn, it is, together with the international search report, published by the International Bureau. The written opinion is not published. |
The procedure under the PCT has great advantages for the applicant, the patent offices and the general public:
(i) the applicant has up to 18 months more than he has in a procedure outside the PCT to reflect on the desirability of seeking protection in foreign countries, to appoint local patent agents in each foreign country, to prepare the necessary translations and to pay the national fees; he is assured that, if his international application is in the form prescribed by the PCT, it cannot be rejected on formal grounds by any designated Office during the national phase of the processing of the application; on the basis of the international search report or the written opinion, he can evaluate with reasonable probability the chances of his invention being patented; and the applicant has the possibility during the international preliminary examination to amend the international application to put it in order before processing by the designated Offices; (ii) the search and examination work of patent offices can be considerably reduced or virtually eliminated thanks to the international search report, the written opinion and, where applicable, the international preliminary examination report that accompany the international application; (iii) since each international application is published together with an international search report, third parties are in a better position to formulate a well-founded opinion about the patentability of the claimed invention. |
The PCT created a Union. The Union has an Assembly. Every State party to the PCT is a member of the Assembly. Among the most important tasks of the Assembly are the amendment of the Regulations issued under the Treaty, the adoption of the biennial program and budget of the Union and the fixing of certain fees connected with the use of the PCT system.
|
Details concerning the PCT can be most simply obtained by consulting the Protecting your Inventions Abroad: Frequently Asked Questions about the Patent Cooperation Treaty, PCT Applicant's Guide and the PCT Newsletter, published by WIPO.
|

Benefits of PCT Filing
- Brings the world within reach
- Postpones the major coast associated with internationalizing a patent application
- Provides a strong basis for patenting decisions
- Is used by the world's major corporations, universities and research institutions when they seek international patent protection
- Allows you to apply securely and easily online, and to save money by doing so : (Click here) Source: WIPO
Procedure EXAMPLE OF MALAYSIA TAKEN
PCT Procedure
|
There are two ways in which an invention can be protected abroad. It can either apply directly to those countries of interest, or use the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT international application).
|
The PCT is an agreement between countries that they will co-operate in order to ease the process of applying for patents in a number of countries around the world. The system is administered by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) from its headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland.
|
The PCT system enables the applicant to make a single application in Malaysia (the international application) and then ‘designate' as many other countries that are involved in the PCT. The PCT system is a patent ‘filing' system, not a patent ‘granting' system. There is no PCT patent or international patent.
|
PCT International Application
|
The Intellectual Property Corporation of Malaysia (MyIPO) acts as a Receiving Office. The PCT application should contain the following :
|
All international applications file with MyIPO must be in the English language; as either a paper based application (in 3 copies) ; or an electronic application (using WIPO's ePCT electronic filing).
|
Please visit the WIPO website to create your ePCT account and obtain your digital certificate, also to read further about ePCT ( https://pct.wipo.int/LoginForms/epct.jsp )
|
The application form may be posted directly to us or hand delivery at our Head Office in Kuala Lumpur ; or lodge them at any branch Offices in Sabah or Sarawak.
|
Fees
|
There are three main fees that must accompany the application. These are the transmittal fee, the international filing fee and the search fee. The transmittal fee covers the work completed by MyIPO, the international filing fee covers the work completed by WIPO and the search fee covers the work completed by an International Searching Authority (ISA).
|
MyIPO collects the transmittal fee but the two other fees are sent to the WIPO and ISA respectively. All fees must be paid in Malaysian Ringgit (RM).
|
International Search Report
|
An International Searching Authority (ISA) is to undertake an international search, that is, to identify any ‘prior art' or written material in determining whether or not the invention is new. The results of the international search can help the applicant to evaluate his chances of getting a patent in the countries that he designates.
|
The following ISAs specify by MyIPO that will undertake the international search :
|
Publication
|
All applications are published usually eighteen months after the application date or priority date if the applicant claiming priority. WIPO produces a journal called the PCT Gazette, which is published every week. It contains the summary page of all applications. The PCT Gazette is also available on the WIPO Internet site.
|
International Preliminary Examination
|
If the applicant choose to have an international preliminary examination, an International Preliminary Examining Authority (IPEA) will undertake it. The applicant must make a specific ‘demand' , and should be submitted directly to the IPEA. The IPEA will examine the application and send an international preliminary examination report which will give the applicant an opinion on whether his invention suitable for a patent to be granted.
|
The following IPEAs specify by MyIPO that will undertake the international preliminary examination :
|
The National Phase
|
The applicant has to enter the national phase in order his international application to proceed separately in any or all of the countries which are party to the PCT. The applicant has up to 30 months after his priority date to enter the national phase in Malaysia.
|
The applicant should notify MyIPO by :
|
|
A PCT patent application is not a primary patent application (i.e. it does not obtain a granted patent covering a number of countries), but rather provides a route to file a central application which is converted to national and regional applications (listings of each given here) and so allows the inventor to delay the filing of these patent applications. This gives the inventor time to test the invention, raise capital & decide in which markets the invention is likely to be successful. Over 130 regional and national offices are covered by the PCT (coloured in blue in the map below). Filing international applications with the PCT is becoming increasingly popular, with the two millionth application filed recently.
PCT contracting states as of April 2010
Main Objectives of the PCT
- To lodge one application, with one Office and in one language,
- Formal examination by a single patent office,
- Good International search & examination reports,
- Provides more time to the applicant.
A priority patent application for an invention is filed in one country, and after the priority date is obtained, a PCT issued by WIPO may be used to preserve the right to file the same invention in each country under the PCT. The PCT claims the priority date from the initial patent application. An international search report, and international examination (optional) are issued centrally from the PCT application. The PCT application then enters national phase, by far the most expensive aspect of the application process as fees need to be paid to each national patent office during filing, prosecution and maintenance, as well as to local attorneys. The PCT does allow these costs to be deferred, usually for up to 30 months from the priority date. Once the PCT has entered national phase, the resulting applications are treated as national or regional. Individual independent patents may then be granted for each country/region, according to local laws.
What is the PCT Receiving Office?
The Receiving Office is the Intellectual Property office in which you file your initial three copies of your international application with one request form. The Receiving Office will then check the application to ensure you have met all of the formal requirements for the PCT. One copy of the application is retained, one copy is forwarded to the International Bureau (IB) of WIPO, and the final copy (when GB is the Receiving Office) is sent to the EPO who act as the International Searching Authority (ISA) for the application.
PCT Timeline
A simple timeline for the limits for international PCT applications filed on or after 1 January 2004 is shown below. Ahelpful tool to calculate time limits for submission of priority document, international publication and entry into the national/regional phase is available free-of-charge from WIPO.
PCT Timeline
Where to File?
When the PCT application reaches national phase entry, all contracting states bound by the PCT are potential states for filing the national phase application. By thinking carefully about their market, and their resources, the applicant can select a subset of the states to actually file their application into.


RECAP FOR FRESHERS
What are Patents?
Patents are granted for inventing new and useful processes, machines,articles of manufacture or compositions of matter. The inventor is granted limited monopoly rights for 20 years from filing in return for public disclosure of the invention. The monoply gives the inventor the right to exclude others from making, using, offering to sell, or selling the invention.
Types of Patents
Utility patents are the most common and may be granted to anyone who invents or discovers any new and useful process, machine, article of manufacture, or composition of matter, or any new and useful improvement thereof. Patentable processes include software programs, business systems, methods of operating a device, new uses of an old devices, and methods of making a product.
Design patents may be granted to anyone who invents a new, original, and ornamental design for an article of manufacture; and
Plant patents may be granted to anyone who invents or discovers and asexually reproduces any distinct and new variety of plant.
What Protection Do I get?
Once filed, the application is "Patent Pending". This provides notice to competitors, but does not provide any legal protection.
After the patent has been granted, protection lasts for 20 years from the date of filing. The patent marking and number must be applied to the product in order to maximize the right to collect damages in a patent infringement lawsuit.
Patent protection is a little unusual in that it is a "negative" right. The inventor has the right to exclude others from making, using, offering to sell, or selling the invention, but the inventor does not necessarily have the right to make, use, offer for sale, or sell their invention. For example, if you were to patent an improvement on an existing patent, you would be given the negative right over only the improvement. The original inventor has the negative right to prevent you from using the original part, and you have the negative right to prevent the original inventor from usign the improvement. Licensing and the sale of patents allows one or both parties to use both the original technology, plus the improvement.
The Patent Process
Obtaining a patent ideally takes around 18 months from start to finish, but frequently takes far more time. Below are the basic steps for obtaining a patent, but keep in mind the patent process is not a simple one and may include additional steps.
Step 1: Filing a Patent
A patent application is filed with the United State Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO). This can be done by the inventor (Pro Se), but the USPTO recommends it be done by a licensed patent attorney or agent due to the complexity of the process.
The main areas of the application include:
- Drawings: The drawings illustrate the invention, and will be required for most applications.
- Detailed Description: This is a highly detailed written description of the invention that provides enough detail that someone in the same field could create, and use the invention.
- Claims: The claims provide the scope of protection for the patent, and as such are the most important part of the application.
A patent can be filed as a provisional or a non-provisional.
- Provisional: A provisional is typically an incomplete patent used to establish your filing date. It is cheaper than a non-provisional, and gives you 1 year in which to file a non-provisional.
- Non-Provisional: A non-provisional is your finished application that begins the examination process.
Step 2: Patent Examination (Non-Provisional)
Once received by the patent office, the examination process begins. The first review is simply a formality review to make sure everything complies with the requirements. Once that is complete, the application is assigned class/subclass based on the type of technology, and assigned to an examiner. At this point the examiner will then conduct substantive examinations of the application. Through a series of Office Actions and responses, the patent attorney works with the examiner (and modifies the application as needed) to try and get the application allowed.
Step 3: Patent Granted
Once the application has been allowed, the inventor must pay the issue fee and the publication fee, at which point the USPTO grants the patent. In order to maintain the patent protection, maintenance fees are due at 3.5, 7.5 and 11.5 years. Failure to pay the fees will result in the patent being abandoned, at which point protection is lost.

- Time 0, file in any 1 country part of PCT (patent cooperation treaty group); get prior art protection from this date. 12 months to improve application, get more data.
- 12 months get search report and written opinion, can amend claims – full filing (PCT), 20yr patent lifetime from here.
- 18 months publication of patent application, protection from infringement
- 30 months nationalisation stage, file in individual countries of choice, can enforce from here



