
Afatinib dimaleate, Dr Reddy's, New patent, WO-2016027243,
DR. REDDY’S LABORATORIES LIMITED [IN/IN]; 8-2-337, Road No. 3, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad, Telangana, India - 500034. Hyderabad 500034 (IN)
RAMAKRISHNAN, Srividya; (IN).
PEDDY, Vishweshwar; (IN).
MAHAPATRA, Sudarshan; (IN).
KANNIAH, Sundara Lakshmi; (IN).
CHENNURU, Ramanaiah; (IN).
JOSE, Jithin; (IN).
DHAGE, Yogesh Mohanrao; (IN).
PEDDIREDDY, Subba Reddy; (IN).
YARRAGUNTLA, Sesha Reddy; (IN).
RAGHUVEER, Sherial; (IN).
KOLLA, Srinivasa Rao; (IN).
ANIL KSHIRSAGAR, Shivani; (IN).
JAFAR SHAIKH, Latif; (IN).
BANDARU, Srinivasulu; (IN)
PEDDY, Vishweshwar; (IN).
MAHAPATRA, Sudarshan; (IN).
KANNIAH, Sundara Lakshmi; (IN).
CHENNURU, Ramanaiah; (IN).
JOSE, Jithin; (IN).
DHAGE, Yogesh Mohanrao; (IN).
PEDDIREDDY, Subba Reddy; (IN).
YARRAGUNTLA, Sesha Reddy; (IN).
RAGHUVEER, Sherial; (IN).
KOLLA, Srinivasa Rao; (IN).
ANIL KSHIRSAGAR, Shivani; (IN).
JAFAR SHAIKH, Latif; (IN).
BANDARU, Srinivasulu; (IN)
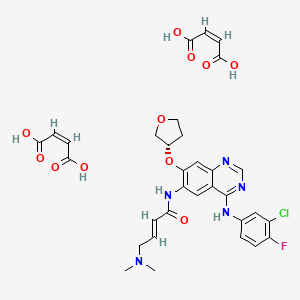
The drug compound having the adopted name afatinib dimaleate, has a chemical name N-[4-[(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)amino]-7-[[(3S)-tetrahydro-3-furanyl]oxy]-6-quinazolinyl]-4-(dimethylamino)-,(2E)-, (2Z)-2-butenedioate (1 :2), and is represented by structure of formula I

Formula I
Afatinib dimaleate is an anticancer protein kinase inhibitor indicated for treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. Process for preparation of afatinib, afatinib dimaleate and intermediates useful in preparation of afatinib dimaleate are described in US Patent Nos. 7,019,012; 8,426,586 and 7,960,546.
US Patent No. 8,426,586 discloses crystalline Form A of afatinib dimaleate salt and processes for preparation thereof. US Patent Application Publication No. 20140051713 discloses crystalline Form B of afatinib dimaleate salt and processes for preparation thereof. PCT Application Publication No. 2013052157 discloses crystalline Form C, Form D and Form E of afatinib dimaleate salt and processes for preparation thereof. The PCT publication also discloses crystalline Form A, B, C and Form D of afatinib base.
Polymorphism, the occurrence of different crystal forms, is a phenomenon of some molecules and molecular complexes. A single molecule may give rise to a variety of polymorphs having distinct crystal structures and physical properties. Polymorphs in general will have different melting points, thermal behaviors (e.g. measured by thermogravimetric analysis - "TGA", or differential scanning calorimetry - "DSC"), X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD or powder XRD) pattern, infrared absorption fingerprint, and solid state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrum. One or more of these techniques may be used to distinguish different polymorphic forms of a compound.
Discovering new polymorphic forms, hydrates and solvates of a pharmaceutical product can provide materials having desirable processing properties, such as ease of handling, ease of processing, storage stability, and ease of purification or as desirable intermediate crystal forms that facilitate conversion to other polymorphic forms. New polymorphic forms and solvates of a pharmaceutically useful compound or salts thereof can also provide an opportunity to improve the performance characteristics of a pharmaceutical product. It enlarges the repertoire of materials that a formulation scientist has available for formulation optimization, for example by providing a product with different properties, e.g., better processing or handling characteristics, improved dissolution profile, or improved shelf-life. For at least these reasons, there is a need for additional solid state forms of Afatinib di-maleate.
SUMMARY
The present application provides novel solid state forms of Afatinib di-maleate, processes for preparing them, and pharmaceutical compositions containing them.
The present application also encompasses the use of novel solid state forms of Afatinib di-maleate provided herein, for the preparation of other afatinib salts, other solid state forms of afatinib dimaleate, and formulations thereof.
The present application also encompasses the use of any one of the novel solid state forms of Afatinib di-maleate disclosed herein for the preparation of a medicament, preferably for the treatment of cancer, particularly for the treatment of cancers mediated by epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and human epidermal receptor 2 (HER2) tyrosine kinases, e.g., solid tumors including NSCLC, breast, head and neck cancer, and a variety of other cancers mediated by EGFR or HER2 tyrosine kinases. The present invention further provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising any one of the Afatinib di-maleate crystalline forms of the present invention and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient.
The present application also provides a method of treating cancer, comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of at least one of the Afatinib di-
maleate novel solid state forms of the present application, or at least one of the above pharmaceutical compositions to a person suffering from cancer, particularly a person suffering from a cancer mediated by epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and human epidermal receptor 2 (HER2) tyrosine kinases, e.g., solid tumors including but not limited to NSCLC, breast, head and neck cancer, and a variety of other cancers mediated by EGFR or HER2 tyrosine kinases.
Example 1 : Preparation of amorphous form of afatinib dimaleate.
2.0 g of afatinib dimaleate was dissolved in 80 mL of a mixture of methanol and acetone (3:1 ) at 26°C and stirred for 15 min. The solution was filtered to remove the undissolved particles and the filtrate was distilled under reduced pressure at 50°C. After distillation the solid was dried under vacuum at 45°C to get 1 .29 g of amorphous afatinib dimaleate. PXRD pattern: Fig. 1 .
///////Afatinib dimaleate, Dr Reddy's, New patent, WO-2016027243, WO 2016027243
