 | |
 |

Lurasidone hydrochloride, Jubilant Life Sciences Ltd, WO 2016059649, New patent
An improved process for the preparation of lurasidone hydrochloride
Jubilant Life Sciences Ltd
WO 2016059649
JUBILANT GENERICS LIMITED (FORMERLY JUBILANT LIFE SCIENCES DIVISION) [IN/IN]; Plot 1A, Sector 16 A, NOIDA Uttar Pradesh 201301 (IN)
MISHRA, Vaibhav; (IN).
DUBEY, Shailendr; (IN).
SINGH, Kumber; (IN).
CHOUDHARY, Alka Srivastava; (IN).
VIR, Dharam; (IN)
DUBEY, Shailendr; (IN).
SINGH, Kumber; (IN).
CHOUDHARY, Alka Srivastava; (IN).
VIR, Dharam; (IN)


Disclosed herein is an improved process for the preparation of Lurasidone and its pharmaceutically acceptable salts via novel intermediate and use thereof for the preparation of an antipsychotic agent useful for the treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Further, present invention provides a cost effective and eco-friendly process for producing Lurasidone hydrochloride of formula (I) substantially free of residual solvent(s) at industrial scale.
Improved process for preparing lurasidone or its hydrochloride, substantially free of residual solvent, useful for treating schizopherenia and bipolar disorder. Also claims novel intermediate of lurasidone eg ((R,R)-cyclohexane-1,2-diyl)bis((1H-imidazol-1-yl)methanone) and its preparation method.

In April 2016, Newport Premium™ reported that Jubilant Life Sciences was capable of producing commercial quantities of lurasidone and lists the drug as a molecule available under research and development on the company's website.
This is the first patenting to be seen from Jubilant Life Sciences that focuses on lurasidone – it having been developed and launched by Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma and EU licensee Takeda, for treating schizophrenia.

May 2, 2014
Neeraj Agrawal: Took charge of API business for Jubilant Life Sciences at the age of 31
Position: CEO Generics, Jubilant Life Sciences
Education: IIIM-C, MBA, 1998; IIT, Bombay, Electrical Engg., 1995.
Previous Jobs: Associate-Business Strategy, Operations Improvement, McKinsey & Co.
Claim to Fame: Took charge of the API business for Jubilant when he was just 31-years-old
Management mantra: It revolves around trust, freedom and teams. I like my team to think and act like an entrepreneur - assess business risks and rewards suitably and then take decisions.
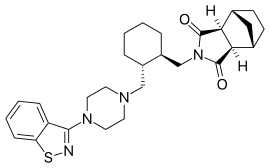
Lurasidone and its pharmaceutically acceptable salts like lurasidone hydrochloride is chemically, (3a ?,45,7 ?,7a5)-2-{ (1 ?,2 ?)-2-[4-(l,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)piperazin-lyl-methyl] cyclohexylmethyl }hexahydro-4,7-methano-2H-isoindole- 1 ,3 -dione hydrochloride and has the structure represented by the Formula (I):

Formula-I
Lurasidone hydrochloride is marketed in the United States under the trade name Latuda®. Lurasidone and its pharmaceutically acceptable salts as well as process for their preparation was first disclosed in US patent no. 5,532,372. The patent discloses the preparation of lurasidone hydrochloride using racemic trans 1,2-cyclohexane dicarboxylic acid. Racemic trans 1,2-cyclohexane dicarboxylic acid on reduction with lithium aluminium hydride in THF at reflux temperature forms l,2-bis(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexane which is converted into racemic iran5-l,2-bis(methanesulfonyloxymethyl)cyclohexane by reaction with methane sulfonyl halide. l-(l,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)piperazine on reaction with trans-l, 2-b (methanesulfonyloxymethyl)cyclohexane in the presence of sodium carbonate and acetonitrile forms iran5-3a,7a-octahydroisoindolium-2-spiro- -[4'-(l,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)]piperazine methanesulfonate which on reaction with bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-2-exo-3-exo-dicarboximide in the presence of potassium carbonate, dibenzo-18-crown-6-ether and xylene on refluxing forms racemic lurasidone free base. The compound is obtained by column chromatography and then treated the resulting lurasidone free base with IPA.HCl in acetone to obtain racemic lurasidone hydrochloride. Resolution of racemic lurasidone hydrochloride is carried out using tartaric acid as resolving agent. The process involves use of lithium aluminium hydride which is highly pyrophoric reagent and is not to utilize the same on commercial scale due to its handling problems associated with its reactivity. Also, the use of the column chromatography for purification is not viable on commercial scale. Further the process involves the usage of dibenzo-18-crown-6-ether as a phase transfer catalyst which is costly material and in turn increases the cost of production. Carrying out the resolution in the last stages is difficult due to the presence of six chiral centres in lurasidone and is also not suitable for an industrial scale preparation as it affects the overall yield and cost of the manufacturing process.

Chinese patent application no. CN102731512 discloses a process for preparation of lurasidone which comprises reaction of racemic irans-l,2-bis(methanesulfonyloxymethyl) cyclohexane and l-(l,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)piperazine in toluene in the presence of sodium carbonate or potassium carbonate having particle size less than 200 micron and tetrabutyl ammonium bromide to give the intermediate /rans-3a,7a-octahydroisoindolium-2-spiro- -[4'-(l,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)]piperazinemethanesulfonate which on reaction with bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-2-exo-3-exo-dicarboximide in toluene using potassium carbonate having particle size less than 200 micron forms racemic lurasidone free base. The racemic free base is converted into racemic hydrochloride salt using acetone and cone, hydrochloric acid. Racemic lurasidone hydrochloride is resolved by following the method disclosed in US patent no. 5,532,372. The process involves resolution of product in the last stage which is not commercially viable as it affects the overall yield and cost of the manufacturing process.
Japanese patent no. JP4219696 discloses the resolution of trans 1,2-cycloheaxne dicarboxylic acid using (lS,2R)-(+)-norephedrine or (lR,2S)-(-)norephedrine to provide (R,R)-trans 1 ,2-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid. The (R,R)-iran,sl,2-cyclohexane dicarboxylic acid obtained was esterified with ethanol and the obtained ester compound was reduced with vitride to provide (R,R)-l,2-bis(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexane followed by treatment with methane sulfonyl chloride to form (R,R)-1,2-bis(methanesulfonyloxymethyl)cyclohexane. The process requires large quantity of reducing agent viz., for reducing one lg of compound about 5g of reducing agent is required which is not conducive for industrial production.
Chinese patent application no. CN 102952001 discloses a process for the preparation of (lR,2R)cyclohexane-l,2-dimethanol by the reduction of (lR,2R)cyclohexane-l,2-
dicarboxylic acid using sodium borohydride or potassium borohydride and boron triflouoride diethyl ether in THF or diethyl ether as solvent. Boron triflouoride diethyl ether is used in large quantity and quite expensive which makes the process commercially unviable.
International publications no. WO 2012/131606 and WO 2014/037886 disclose a process for preparation of lurasidone which involves separating the racemic transl,2-cyclohexane dicarboxylic acid into its (R,R) trans and (S,S) trans isomers and then using the desired trans (R,R) isomer for the preparation of lurasidone hydrochloride using the chemistry disclosed in US patent no. 5,532,372 for preparation of racemic lurasidone hydrochloride. In these publications diisobutyl aluminium hydride (DIBAL) is used as the reducing agent for the preparation of (1R,2R) cyclohexane 1,2-dimethanol from (1R,2R) cyclohexane 1,2-dicarboxylic acid which is quite expensive. Further the process involves the usage of dibenzo-18-crown-6-ether as a phase transfer catalyst which is costly material and in turn increases the cost of production.
Some of the prior art processes disclose the process for the preparation of lurasidone hydrochloride from l,2-(lR,2R)-bis-(methanesulfonyloxymethyl)cyclohexane using different solvents and bases.
US patent no. 8,853,395 discloses a process for the preparation of lurasidone in which condensation of iran5-l,2-bis(methanesulfonyloxymethyl)cyclohexane with 1-(1,2-benz isothiazol-3-yl)piperazine and condensation of /rans-3a,7a-octahydroisoindolium-2-spiro- -[4'-(l,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)]piperazine methanesulfonate with bicyclo[2.2.1] heptane-2-exo-3-exo-dicarboximide is carried out using organic bases with a ρ¾ higher than 10 such as l,4-diazabicycloundec-7-ene (DBU), l,5-diazabicyclo[4.3.0]non-5-ene (DBN), 1,4-diaza bicyclo[2.2.2] -octane (DABCO). These organic bases are comparatively expensive.
Indian patent application no. IN 2306/MUM/2014 and Chinese patent applications no. CN 102863437 and CN 103864774 disclose the use of dimethyl formamide (DMF), dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO), dimethyl acetamide (DMA) and N-methyl pyrrolidine (NMP) for the condensation of iran5-3a,7a-octahydroisoindolium-2-spiro- -[4'-(l,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)] piperazine methanesulfonate with bicyclo[2.2.1] heptane-2-exo-3-exo-dicarboximide to form lurasidone. These solvents have high boiling point so not preferred at commercial scale.
Some of the prior art processes are related to reduction of impurities or quality improvement of lurasidone hydrochloride.
International publication no. WO2011/136383 discloses a process for the preparation of lurasidone hydrochloride in which amount of by products are reduced by increasing the quantity of l-(l,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)piperazine instead of sodium carbonate or potassium carbonate as base in the reaction mixture. Increasing the amount of l-(l,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)piperazine causes an increase in cost of production and removal of excess compound makes the process less commercially viable.
International publication no. WO2011/136384 discloses a process for the preparation of lurasidone hydrochloride in which amount of by products are reduced by using dibasic potassium phosphate with a small amount of water as a base instead of sodium carbonate. Use of dibasic potassium phosphate as a base causes an increase in cost of production as dibasic potassium phosphate is expensive.
International publication no. WO2013/014665 discloses various processes for the preparation of lurasidone hydrochloride. In general the process is shown below:

Formula-(I)
In this process iran5-(lR,2R)-2-(aminomethyl)cyclohexyl)methanol of Formula (B) is first reacted with bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-2-exo-3-exo-dicarboximide of Formula (A) to form (3aR,4S,7R,7aS)-2-(((lR,2R)-2-(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexyl)methyl)hexahydro-lH-4,7-methanoisoindole-l,3(2H)-dione of Formula (C) which on reaction with methane sulphonyl chloride followed by reaction with l-(l,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)piperazine of Formula (D) forms lurasidone free base which was converted into lurasidone hydrochloride using acetone and cone, hydrochloric acid.
Some of the prior art processes disclose various combinations of hydrogen chloride and solvent for the preparation of lurasidone hydrochloride from lurasidone free base.
US 7,605,260 discloses use of acetone and aqueous HC1 having strength 1.8-14.4 % for preparing lurasidone hydrochloride. The yield of lurasidone hydrochloride is relatively low (85%) by this method. If the acid concentration during the salt formation is more than 5.0% then acetone quantity as the residual solvent in the reaction product is found to be greater than 0.5% in our hands which is above the ICH limits. If acid concentration during the salt formation is less than 1.8%, then yield is reduced drastically to 65%. Therefore, this method has limitations on the large-scale industrial production.
Chinese patent application no. CN102746289A discloses the process for the preparation of lurasidone hydrochloride by adding a mixture of acetone and aqueous HC1 to a solution of lurasidone free base in acetone. On reproducing this process in laboratory, it was observed that the XRPD of the product obtained does not match with XRPD of lurasidone hydrochloride.
Indian patent application IN 777/MUM/2013 discloses use of IPA, water and 35% Aqueous HC1 for the preparation of lurasidone hydrochloride. The IPA content in the product was found to be more than 5000ppm.
The methods described in the prior art are not suitable for large scale commercial production as the residual solvent is out of the ICH limits and thus the product obtained can't be used as a drug. In order to keep the residual solvent(s) within ICH limits, repeated crystallization/purification are required which results in reduced yield and make the process quite expensive.
The prior art discloses various processes for the preparation of lurasidone hydrochloride and its intermediates. However, there still remains a need for alternative process for the preparation of lurasidone and its pharmaceutically acceptable salts substantially free of residual solvent(s) which can be used as a drug.
According to another embodiment of the present invention, novel process for the preparation of the compound of Formula (III), their isomers and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, comprises condensing 1,2-cyclohexane dicarboxylic acid of Formula (II), their isomers with carbonyl diimidazole, optionally in a solvent.
(IV) 

Formula (III)
NaBH4 RT /H20
Formula (VII)
Scheme-1:

Example-1
Synthesis of trans(R,R)-l,2-cyclo exane dicarboxylic acid
A round bottom flask was charged with methanol (500 mL), IPA (500 mL) and trans (racemic)-l,2-cyclohexane dicarboxylic acid (100 g). In this reaction mass (R)-l-phenylethyl amine (74 mL) was added over a period of 30 minutes and stirred for 2-3 hrs at 30-40 °C. The solid obtained was filtered, washed with methanol and IPA solution (50+50 mL) and dried under reduced pressure to obtain crude salt of iran5(R,R)-l,2-cyclohexane dicarboxylic acid. The obtained salt was stirred in a solution of methanol (500 mL) and IPA (500 mL) at 65-70 °C for 2-3 hours, cooled to room temperature and filtered. The solid was washed with methanol and IPA solution (50+50 mL) and dried under reduced pressure. The solid thus obtained was dissolved in about 2N hydrochloric acid and extracted two times with ethyl acetate (1000 mL+200 mL). Organic layers were combined and washed with brine solution (100 mL). Ethyl acetate was distilled off under vacuum at 50-55 °C and cyclohexane was added to the residue. The solid separated out was filtered and washed with cyclohexane and dried under vacuum at 45-50 °C for 8-10 hours. Yield = 29.4 g
Example-2
Synthesis of ((R,R)-cyclohexane-L2-diyl)bis((lH-imidazol-l-yl)methanone)
To a solution of iran5(R,R)-l,2-cyclohexane dicarboxylic acid (25.0 g) in THF (250 mL), carbonyl diimidazole (60 g) is added and stirred for one hour at 25-30 °C . To the said solution of (R,R)2-(((lH-imidazole-lcarbonyl)oxy)carbonyl)cyclohexanecarboxylic acetic anhydride lH-imidazole (25.0 g) in THF (250 mL) is stirred for one hour at 45-50 °C. The compound obtained is isolated and is characterized by mass and NMR.
[m z = 272.75; 1H-NMR: 8.24 (s, 2H), 7.72 (d, 2H); 7.50 (d, 2H), 3.5 (m, 2H), 2.26-1.50 (m, 8H)]
Example-3
Synthesis of tra»,s(R,R)-l,2- bis(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexane
To a solution of ((R,R)-cyclohexane-l,2-diyl)bis((lH-imidazol-l-yl)methanone) (25 g) in THF (250 mL), sodium borohydride (22.0 g) followed by water (44.0 mL) are added and stirred for one hour. To this reaction mass, 10% solution of acetic acid (500 mL) and dichloromethane (500 mL) are added, stirred and layers separated. The organic layer is washed with 10% sodium bicarbonate solution followed by water. The dichloromethane is distilled off from organic layer under vacuum to give an oily mass. To the oily mass
dichloromethane (100 mL), water (100 mL) and 12.5mL cone, hydrochloric acid (35%) are added, stirred and layers obtained are separated. The dichloromethane is distilled off completely from organic layer at 40 °C to obtain oily mass (15.5 g).
Example-4
One pot process for synthesis of trans(R,R)-l,2- bis(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexane from trans(R,R)-l,2-cyclo exane dicarboxylic acid
To a solution of iran5(R,R)-l,2-cyclohexane dicarboxylic acid (25.0 g) in THF (250 mL), carbonyl diimidazole (60 g) was added and stirred for one hour at 25-30 °C. To the intermediate obtained sodium borohydride (22.0 g) and water (44.0 mL) were added and stirred for one hour. To this reaction mass, 10% solution of acetic acid (500 mL) and dichloromethane (500 mL) were added, stirred and layers separated. The aqueous layer was washed with dichloromethane (250 mL). The organic layer was washed with 10% sodium bicarbonate solution followed by water. The dichloromethane is distilled off from organic layer under vacuum to give an oily mass. To the oily mass dichloromethane (100 mL), water (100 mL) and 12.5mL cone, hydrochloric acid (35%) were added, stirred and layers obtained were separated. The dichloromethane was distilled off completely at 40 °C to obtain oily mass (15.5 g).
Example-5
Synthesis of m¾ns(R,R)- 2-bis(methanesulfonylmethyl) cyclohexane
To a suspension of irafts(R,R)-l,2-bis(hydroxymethyl)cyclohexane (15.0g) in dichloro methane (300 mL), triethyl amine (43.7 mL) followed by methane sulphonyl chloride (17.8 mL) were added over a period of 30-45 minutes. Reaction mass was stirred for 2-3 hrs. Reaction was monitored by HPLC (RI detector). After the completion of reaction, water was added, stirred and layers separated. The organic layer was washed with 10% sodium bicarbonate solution (150 mL) followed by water (150 mL). The dichloromethane was distilled off from organic layer under vacuum at 40-55 °C to give an oily mass. Methanol (30 mL) was added to the oily mass and strip off under vacuum at 40°C, added methanol (150 mL) and stirred for 1 h at 10-15°C and the solid obtained was filtered, washed with methanol (15 mL) and dried under vacuum to get the product (15.8g).
Example-6
Synthesis of ?ran (R,R)-3aJ(¾-octahvdroisoindolium-2-spiro- -r4-(L2-benzoisothiazole-3-yl)l piperazine methanesulfonate:
To a suspension of iran5(R,R)-l,2-bis(methanesulfonylmethyl)cyclohexane (15 g) in acetonitrile (150 mL) l-(l,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)piperazine (10.95g) and sodium carbonate (7.8 g) were added, heated and stirred for 20 hrs at reflux temperature. Reaction was monitored by HPLC. After the completion of reaction, mass was cooled to 40-45 °C, filtered and washed with acetonitrile (20 mL). The acetonitrile was distilled off under vacuum at 45-50 °C. To the residue acetone (100 mL) was added, stirred for 1 hour, filtered, washed with acetone (10 mL), dried at 50-55°C for 6-8 hours to get the product (12.5 g).
Example-7
Synthesis of Lurasidone
To a suspension of iran5(R,R)-3<3,7(3-octahydroisoindolium-2-spiro- -[4-(l,2-benzo isothiazole-3-yl)]piperazinemethanesulfonate (10 g) in toluene (150 mL), bicycle[2.2.1] heptane-2-exo-3-exo-dicarboximide (5.9 g) and potassium carbonate (4.8 g) were added, heated to 110° C and stirred for 8-10 hours. Reaction was monitored by HPLC. After the completion of reaction, reaction mass was cooled to 20-30 °C, filtered and washed with toluene (10 mL). The toluene was distilled off at 55-60°C. To the residue IPA (100 mL) was added and stirred for 1-2 hours at room temperature. Lurasidone free base obtained was filtered and washed with IPA (10 mL). The solid was suck dried for 30 minutes to obtain lurasidone.
Example-8
Synthesis of Lurasidone hydrochloride
To lurasidone base (5g), acetone (75mL) and water (10 mL) were added. The mixture was heated to 55-60°C followed by the addition of IPA.HCl (10%) (lOmL) and stirred for 1-2 hours, reflux temperature. The clear solution obtained was stirred for 30 min and then 5ml IPA.HCl (10%) was added. The reaction mixture was stirred at reflux temperature for 30 min, cooled and stirred for 60 min. The solid obtained was filtered and washed with acetone (5ml) and dried under vacuum at 60°C for 8 hours.
Acetone: 542 ppm; IPA= 38ppm; Yield=93%
Example-9
Synthesis of Lurasidone hydrochloride
To lurasidone base (5g), acetone (75mL) and water (5 mL) were added. The mixture was heated to 55-60°C followed by the addition of IPA.HCl (10%) (5mL) and stirred for about 1-2 hours. The reaction mixture was stirred for 30 min. at 55-60°C, cooled and stirred for 60 min. The solid obtained was filtered and washed with acetone (5ml) and dried under vacuum at 70-80°C for 8 hours.
Address: 18, 56, 57 and 58, KIADB Industrial Area, Nanjangud, Mysuru, Karnataka 571302

Chairman & Managing Director
Jubilant Bhartia Group Shyam, together with his brother Hari, is founder of Jubilant Bhartia Group (www.jubilantbhartia.com) headquartered in New Delhi, India. The Jubilant Bhartia Group, with 30,000 employees, has a strong presence in diverse sectors like Pharmaceuticals and Life Sciences, Oil and Gas (exploration and production), Agri products, Performance Polymers, Retail, Food and Consulting in Aerospace and Oilfield Services. Jubilant Bhartia Group has four flagships Companies- Jubilant Life Sciences Limited, Jubilant FoodWorks Limited and Jubilant Industries Limited, listed on Indian Stock Exchange and Jubilant Energy NV, listed at AIM market of London Exchange.Shyam, holds a bachelors’ degree in commerce from St. Xavier’s College, Calcutta University, and is a qualified cost and works accountant & a fellow member of the Institute of Cost and Works Accountants of India (ICWAI).Shyam has been associated with various institutions and has served as Member of Board of Governors, Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Mumbai, and Indian Institute of Management (IIM), Ahmedabad. Shyam has also served as a Member of the Executive Committee of Federation of Indian Chamber of Commerce & Industry (FICCI) & Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) and was also a member of Task Force on Chemicals appointed by the Government of IndiaShyam’s immense contributions have been recognized by various awards. CHEMEXCIL has conferred Lifetime Achievement Award 2010-11 to him. He, along with his brother, was felicitated with the Entrepreneur of the Year Award at the prestigious AIMA Managing India Awards 2013, presented by the President of India. In 2010, the duo also shared the much-covetedErnst & Young Entrepreneur of the Year Award for Life Sciences & Consumer Products category.Shyam serves on the Board of several Public and Private and Foreign companies likes of Chambal Fertilizers and Chemicals Ltd, Putney Inc., CFCL Technologies Limited (Cayman Islands), Tower Promoters, BT Telecom India Pvt Ltd., American Orient Capital Partners India Pvt Ltd, IMACID, Morocco, Safe Food Corporation, etc. He was also a Director on the Board of Air India.Shyam is a regular participant at the World Economic Forum Annual Meeting in Davos and a member of the Chemical Governors Council of the World Economic Forum.Shyam is married to Shobhana, Former Member of Parliament & Chairperson, The Hindustan Times Media Ltd. They have two sons- Priyavrat and Shamit.
ISO Certification
ISO 9001:2008, 14001:2004 & OHSAS 18001:2007 certified
Code of Conduct
Code Of Conduct for Directors and Senior ManagementThis Code of Conduct highlights the standards of conduct expected from the Company’s Directors and Senior Management so as to align these with the Company’s Vision, Promise and Values.Jubilant Life Sciences Ltd. (Jubilant) has a well formulated Vision which drives the business and has the promise of Caring, Sharing, Growing to all the stakeholders–We will, with utmost care for the environment, continue to enhance value for our customers by providing innovative products and economically efficient solutions and for our shareholders through sales growth, cost effectiveness and wise investment of resources.
Director's Desk

Co-Chairman & Managing Director
Jubilant Bhartia Group
Hari, together with his brother Shyam, is co-founder of Jubilant Bhartia Group (www.jubilantbhartia.com) headquartered in New Delhi, India.The Jubilant Bhartia Group, with 30,000 employees, has a strong presence in diverse sectors like Pharmaceuticals and Life Sciences, Oil and Gas (exploration and production), Agri products, Performance Polymers, Retail, Food and Consulting in Aerospace and Oilfield Services. Jubilant Bhartia Group has four flagships Companies- Jubilant Life Sciences Limited, Jubilant FoodWorksLimited and Jubilant Industries Limited, listed on Indian Stock Exchange and Jubilant Energy NV, listed at AIM market of London Exchange.A Chemical Engineering Graduate from the prestigious Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Delhi, Hari was conferred the Distinguished Alumni award by his alma mater in 2000. He has been associated in various capacities with the IIT system and with the Ministry of Human Resource Development, Government of India.Hari is a past President of the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) & a member of several educational, scientific and technological programmes of the Government of India. He is currently the Chairman of the Board of Governors of the Indian Institute of Management (IIM), Raipur and Member of the International Advisory Board of McGill University, Canada.Hari is the Co-Chairman of India-Canada CEO’s Forum appointed by the Prime Minister of India. He is also a member of CEO’s Forum for India-USA, India-France and India-Sri Lanka and Joint Task Force for India-Myanmar & India-UAE. He is a regular participant at the World Economic Forum Annual Meeting in Davos and is a member of the World Economic Forum’s International Business Council and the Health Governors.Hari’s immense contributions have been recognized by various awards. He, along with his brother, was felicitated with the Entrepreneur of the Year Award at the prestigious AIMA Managing India Awards 2013, presented by the President of India. In 2010, the duo also shared the much-coveted Ernst & Young Entrepreneur of the Year Award for Life Sciences & Consumer Products category.Hari serves on the board of several public and private companies like TV 18 Broadcast Ltd., Shriram Pistons & Rings Ltd., Export Credit Guarantee Corporation of India Ltd., BT Telecom India Pvt. Ltd & India Brand Equity Foundation.Hari is married to Kavita, a leading Fashion Designer and Retailer. They have a daughter, Aashti and a son, Arjun.

Jubilant Bhartia Group
Hari, together with his brother Shyam, is co-founder of Jubilant Bhartia Group (www.jubilantbhartia.com) headquartered in New Delhi, India.The Jubilant Bhartia Group, with 30,000 employees, has a strong presence in diverse sectors like Pharmaceuticals and Life Sciences, Oil and Gas (exploration and production), Agri products, Performance Polymers, Retail, Food and Consulting in Aerospace and Oilfield Services. Jubilant Bhartia Group has four flagships Companies- Jubilant Life Sciences Limited, Jubilant FoodWorksLimited and Jubilant Industries Limited, listed on Indian Stock Exchange and Jubilant Energy NV, listed at AIM market of London Exchange.A Chemical Engineering Graduate from the prestigious Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Delhi, Hari was conferred the Distinguished Alumni award by his alma mater in 2000. He has been associated in various capacities with the IIT system and with the Ministry of Human Resource Development, Government of India.Hari is a past President of the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) & a member of several educational, scientific and technological programmes of the Government of India. He is currently the Chairman of the Board of Governors of the Indian Institute of Management (IIM), Raipur and Member of the International Advisory Board of McGill University, Canada.Hari is the Co-Chairman of India-Canada CEO’s Forum appointed by the Prime Minister of India. He is also a member of CEO’s Forum for India-USA, India-France and India-Sri Lanka and Joint Task Force for India-Myanmar & India-UAE. He is a regular participant at the World Economic Forum Annual Meeting in Davos and is a member of the World Economic Forum’s International Business Council and the Health Governors.Hari’s immense contributions have been recognized by various awards. He, along with his brother, was felicitated with the Entrepreneur of the Year Award at the prestigious AIMA Managing India Awards 2013, presented by the President of India. In 2010, the duo also shared the much-coveted Ernst & Young Entrepreneur of the Year Award for Life Sciences & Consumer Products category.Hari serves on the board of several public and private companies like TV 18 Broadcast Ltd., Shriram Pistons & Rings Ltd., Export Credit Guarantee Corporation of India Ltd., BT Telecom India Pvt. Ltd & India Brand Equity Foundation.Hari is married to Kavita, a leading Fashion Designer and Retailer. They have a daughter, Aashti and a son, Arjun.

Executive Leadership Team
Shyam S Bhartia
ChairmanHari S Bhartia
Co-Chairman & Managing DirectorShyamsundar Bang
Executive Director -Manufacturing & Supply ChainR Sankaraiah
Executive Director - FinancePramod Yadav
Co-CEO
Life Science IngredientsRajesh Srivastava
Co-CEO
Life Science IngredientsG. P. Singh
Fine Chemicals and CRAMS
CEO - Jubilant PharmaChandan Singh
President - Life Science ChemicalsMartyn Coombs
President - Jubilant DraxImageBryan Downey
President - Allergy BusinessT. S. Parmar
President - India Branded PharmaceuticalsDr. Ashutosh Agarwal
Chief Scientific Officer -Chemicals and Life Science IngredientsAjay Khanna
Chief - Strategic & Public Affairs
///////Lurasidone hydrochloride, Jubilant Life Sciences Ltd, WO 2016059649, New patent




























